Plenoptic Laboratory Hard X-Ray System
Volumetric X-ray refraction and scattering imaging
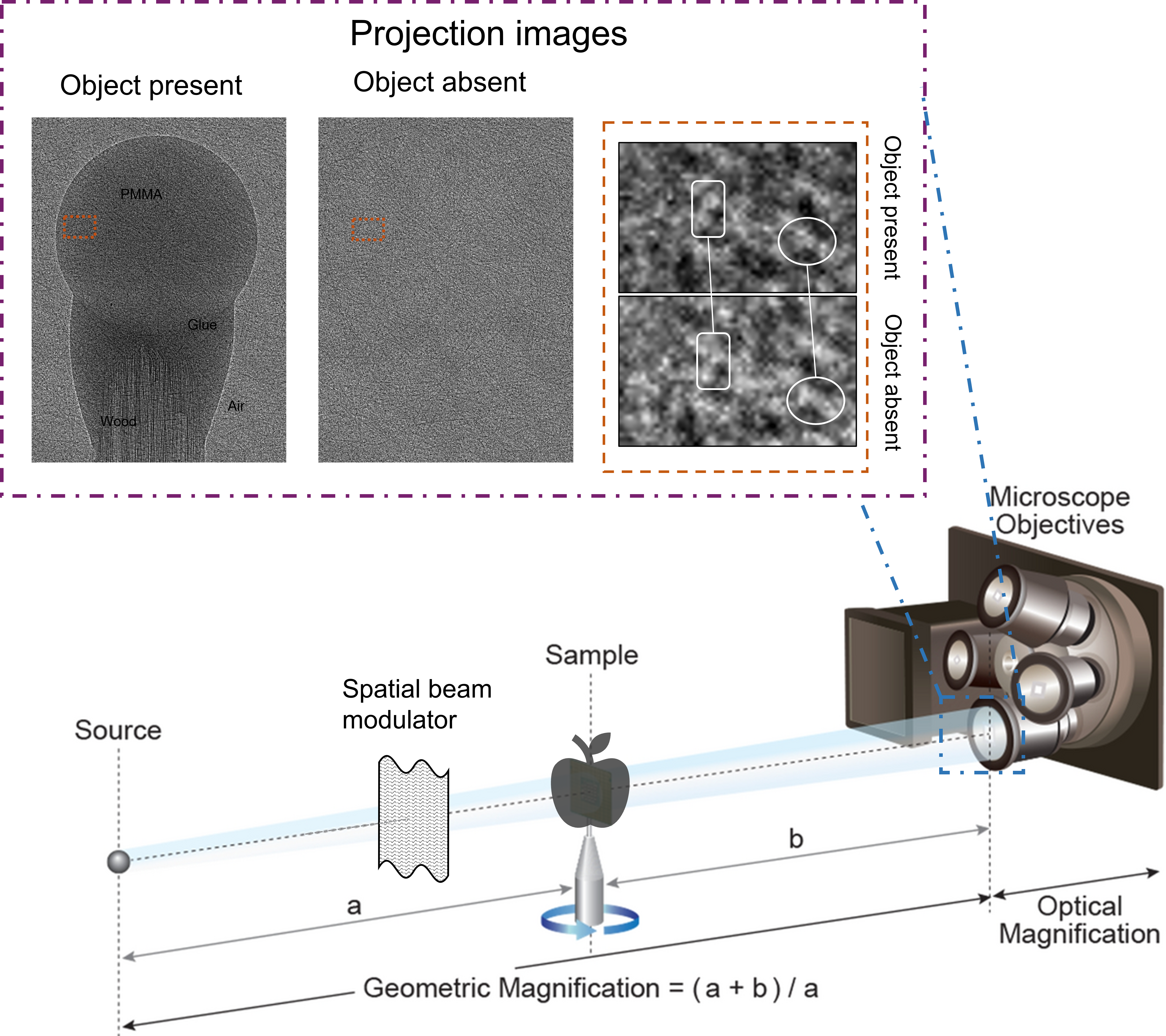
Tomographic X-ray microscopy images 3D objects at micrometer resolution. Beyond standard absorption, capturing phase and scattering signals is crucial for low-density materials. While phase-contrast methods, such as differential phase contrast, become popular in synchrotron facilities around the world, transferring those methods to labs has been challenging primary due to the lack of high-power, high spatial coherence sources. In this work, we report a laboratory system for simultaneous X-ray absorption, phase, and darkfield tomography. The system features an actively liquid-cooled micro-focal X-ray source, a spatial beam modulation mask for generating trackable granular patterns for plenoptic lightfield detection, and a high-resolution X-ray detection module with secondary optical magnification, allowing for a relatively compact implementation with about 20 cm to less than 30 cm source-to-detector distance.
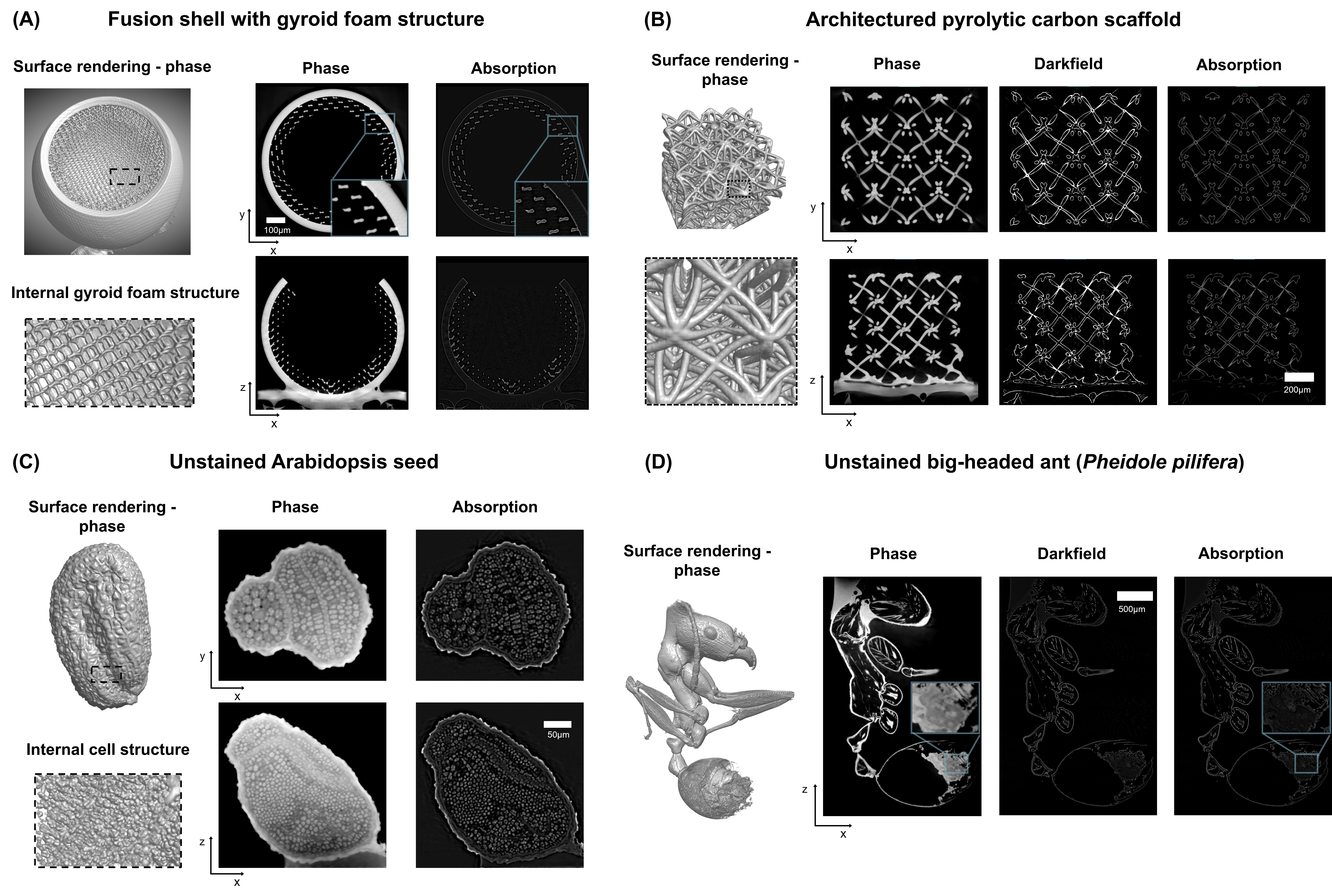
We demonstrate tomographic phase, darkfield, and absorption reconstructions of various small samples. Figure (A) shows a spherical shell with an internal gyroid foam structure, designed for inertial confinement fusion and fabricated using Nanoscribe’s Quantum X system with Two-Photon Grayscale Lithography. The phase reconstruction provides more accurate representation of the foam and shell than absorption imaging. In (B), we show a 3D-printed scaffold for musculoskeletal tissue engineering, manufactured using a pyrolytic process that enables electrical signal conduction to muscle cells. The dark-field image highlights scattering in the carbon material, especially at joint regions.
We also imaged complex life science samples. In (C), we present an unstained Arabidopsis thaliana seed - a widely used model organism in plant biology. This represents, to our knowledge, the first sub-micron lab tomography of an unstained Arabidopsis seed, clearly revealing cell vertices useful for modeling organismal development. In (D), we show reconstructions of an unstained big-headed ant (Pheidole pilifera), with internal organs clearly visible in phase reconstruction cross-sections. We believe this high-resolution, high-contrast imaging system can enable new studies in entomology, paleontology, and materials science by leveraging complementary image signals.
Further reading
Xu, Shiqi, et al. “High-Resolution Multimodal Tomography with a Plenoptic Hard X-Ray Laboratory System.” Computational Optical Sensing and Imaging. Optica Publishing Group, 2025.