Parallelized Diffuse Correlation Imaging
Imaging hemo-dynamics at single photon sensitivity
Noninvasive optical imaging through dynamic scattering media has numerous important biomedical applications but still remains a challenging task. While standard diffuse imaging methods measure optical absorption or fluorescent emission, few works to date, however, have aimed to experimentally measure and process such temporal correlation data to demonstrate deep-tissue video reconstruction of decorrelation dynamics. In this work, a single-photon avalanche diode array camera is utilized to simultaneously monitor the temporal dynamics of speckle fluctuations at the single-photon level from 12 different phantom tissue surface locations delivered via a customized fiber bundle array. Then a deep neural network is applied to convert the acquired single-photon measurements into video of scattering dynamics beneath rapidly decorrelating volume.
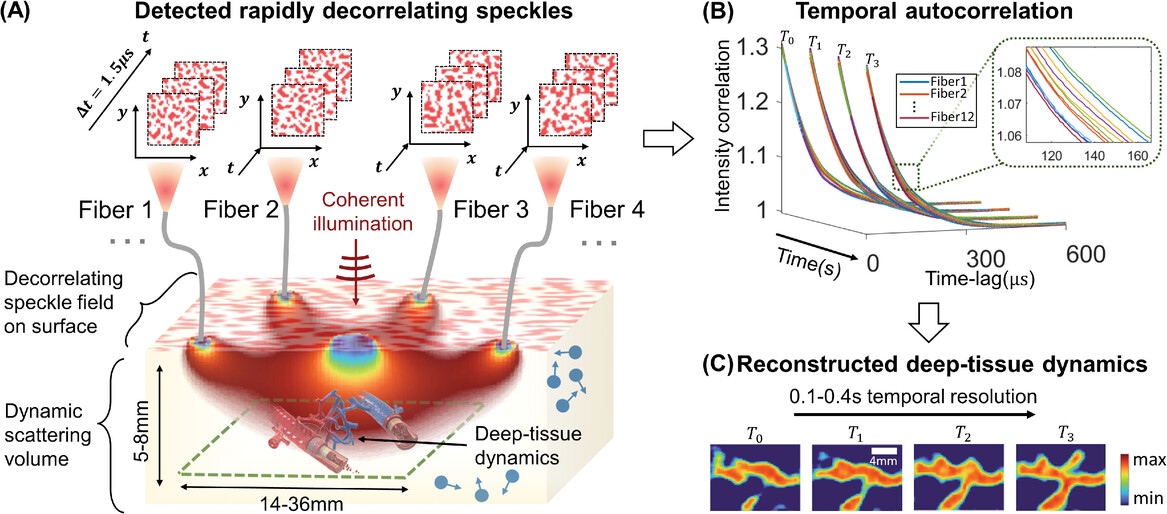
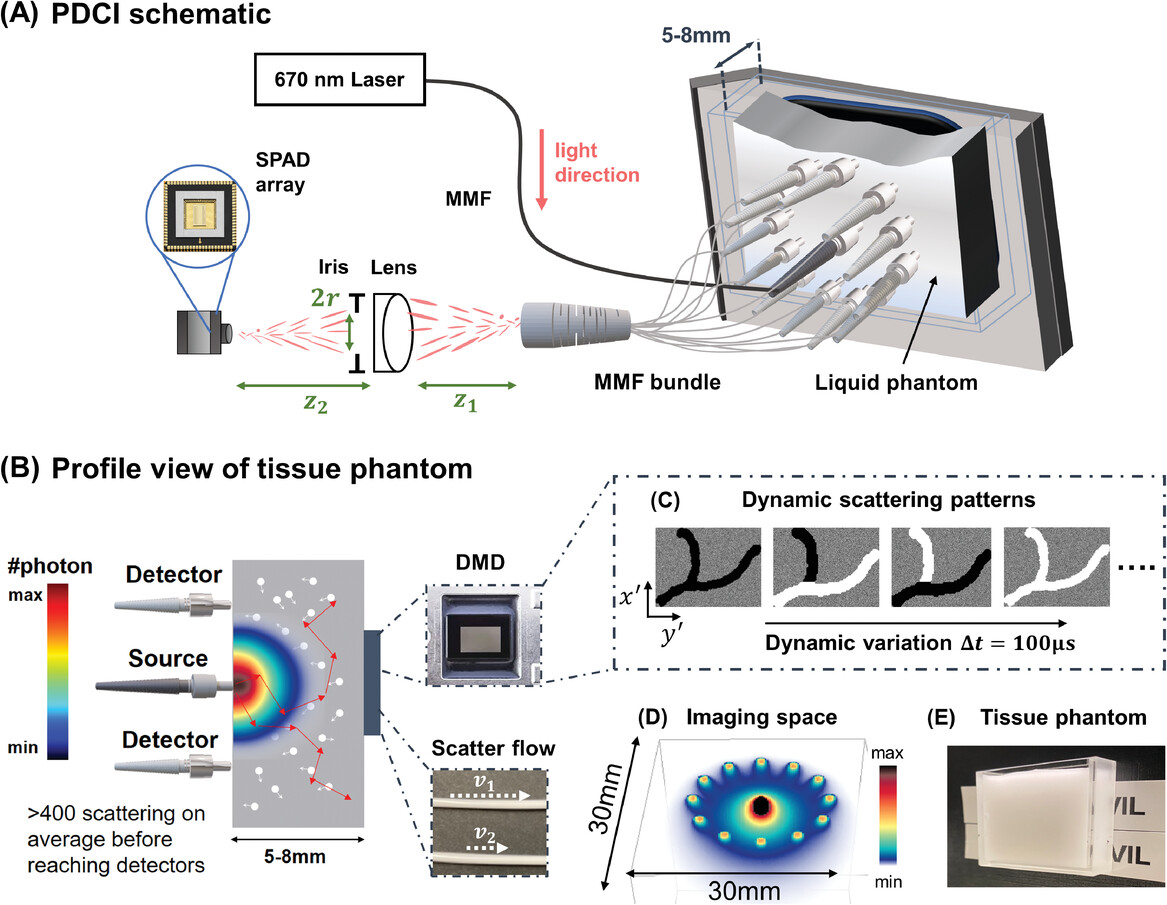
To assess the performance of our PaDI system, we first turn to an easily reconfigurable nonbiological liquid phantom setup that offers the ability to flexibly generate unique image targets with known spatial and temporal properties. To mimic decorrelation rates and scattering properties of human tissue, we utilized a turbid, rapidly decorrelating liquid phantom filled with colloidal polystyrene microspheres solution enclosed in a custom-designed thin-walled cuvette.
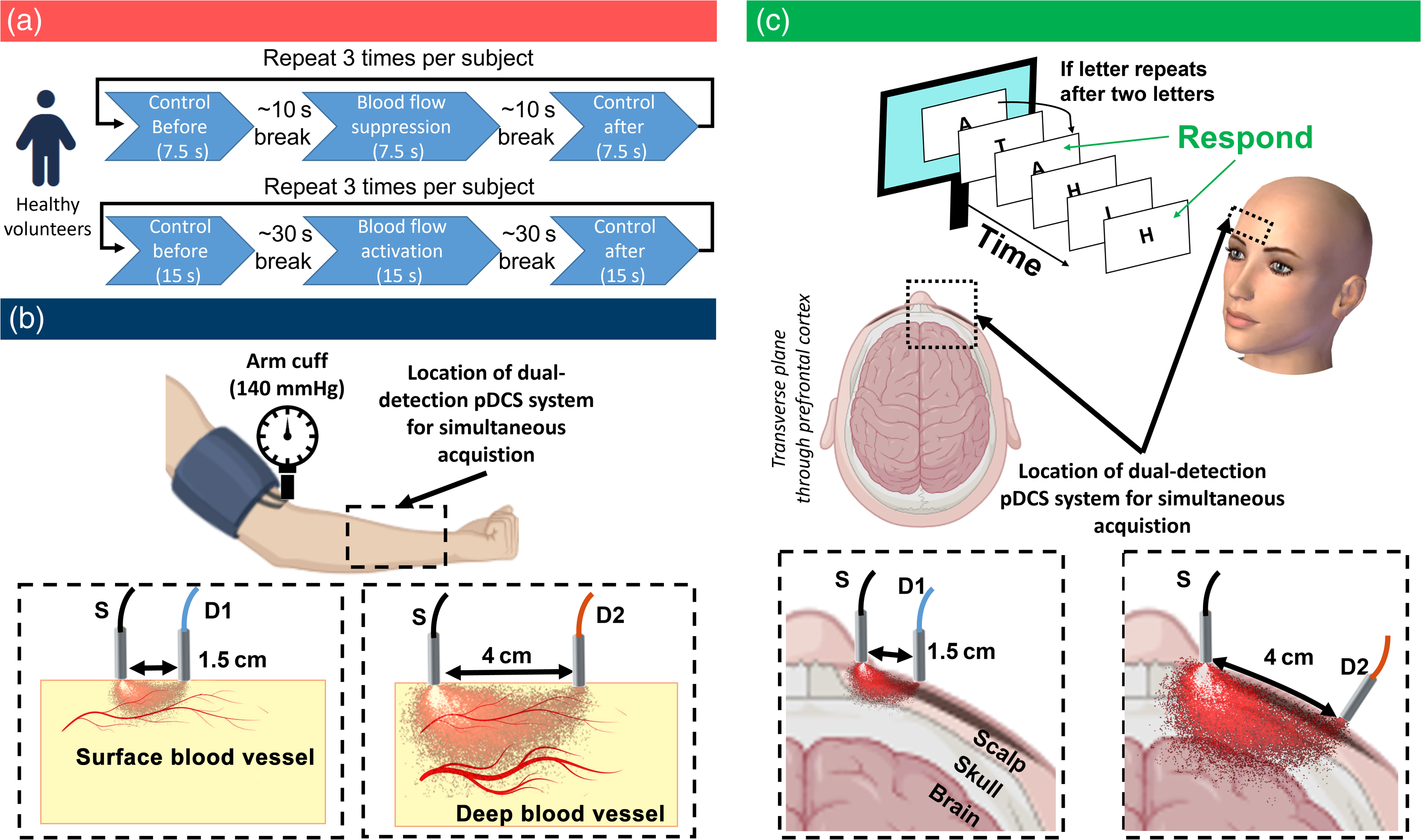
Finally, we extended our method to healthy human subjects in controlled experiments to monitor forearm muscular blood flow during restriction and prefrontal cortex cerebral blood flow during cognitive tasks.
Further reading
Xu, Shiqi, et al. “Imaging Dynamics Beneath Turbid Media via Parallelized Single‐Photon Detection.” Advanced Science 9.24 (2022): 2201885.
Xu, Shiqi, et al. “Transient motion classification through turbid volumes via parallelized single-photon detection and deep contrastive embedding.” Frontiers in neuroscience 16 (2022): 908770.
Kreiss, Lucas, et al. “Beneath the surface: revealing deep-tissue blood flow in human subjects with massively parallelized diffuse correlation spectroscopy.” Neurophotonics 12.2 (2025): 025007-025007.